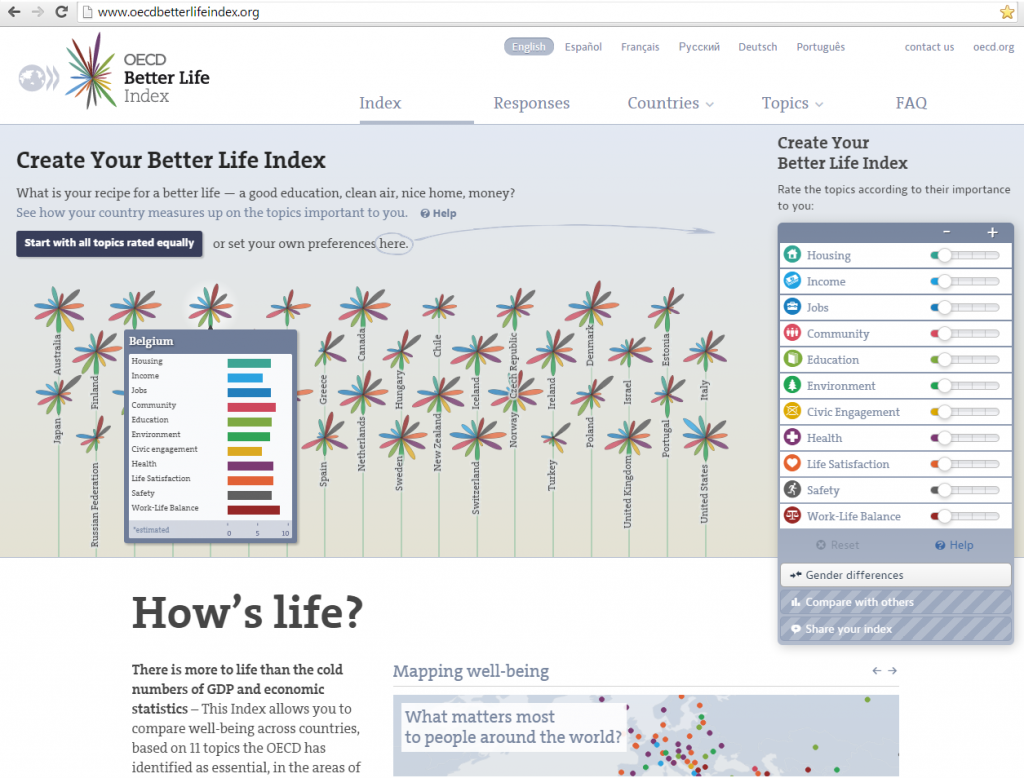
Technology is anything invented after you are born – Alan Kay, computer scientist
If Alan Kay is right, I live in a time with a lot of technology. I am part of the last generation of high school students who wrote their own book reports, instead of copy pasting them from the internet. I am also part of the first generation that communicate with close ones in other countries any moment of the day and anywhere. If needed, with a couple of swipes I can access all knowledge of the world from my toilet.
Am I living in a dystopia or a utopia? The jury is still out on that. But Dave Eggers’ novel The Circle provides some compelling evidence that we are on the wrong way. Over the Christmas holidays, I read his smart novel about a top-notch internet company in which the attentive reader may recognise a type of Google. The Circle has become the leading firm thanks to the creation of a single, and verified online identity – with the Orwellian name TruYou – that allows you to sign in everywhere. This single online identity is the end of password remainder emails and internet trolling.
 The hero of the novel, Mae Holland, is extremely excited when landing a job on the Circle’s campus. She quickly spends her time filling out surveys, her mandatory social media activity, attending all the social gatherings, and occasionally do a bit of work. Responding surveys, whether it is from her own clients as part of the customer relations team, or on the question whether more or less vegan options should be served at lunch, becomes a key part of her daily tasks: her opinion counts. As a result, she almost has too little time to enjoy all the amazing services on campus, ranging from free and high quality healthcare to organic local meals and concerts from famous musicians. Positive and optimistic slogans entice the employees to be active and creative.
The hero of the novel, Mae Holland, is extremely excited when landing a job on the Circle’s campus. She quickly spends her time filling out surveys, her mandatory social media activity, attending all the social gatherings, and occasionally do a bit of work. Responding surveys, whether it is from her own clients as part of the customer relations team, or on the question whether more or less vegan options should be served at lunch, becomes a key part of her daily tasks: her opinion counts. As a result, she almost has too little time to enjoy all the amazing services on campus, ranging from free and high quality healthcare to organic local meals and concerts from famous musicians. Positive and optimistic slogans entice the employees to be active and creative.
It turns a bit nastier when Mae is told to pay more attention to her social media presence. At the Circle, all performance is assessed. All experiences must be shared, and status updates, comments and likes all count towards her Participation Rank (PartiRank). Participation becomes a daily task: it takes multiple hours to rise in the rankings.
The novel is smartly constructed, and it would be a pity to reveal all the details. I’d rather encourage you to read the story itself. But the message is clear: starting with benevolent intentions – ending internet trolling and protecting children, for instance – technology companies get to a position where they gather more and more information about all of us.
It’s all for a good cause: to share wonderful moments with our loved ones. If I want to make a hike in the mountains, aren’t I selfish if I don’t publish the pictures online, so my mother can see them from home? Everything must be known, claims the lead evangelist at the Circle. And that quickly turns into an Orwellian situation. If everything must be known, are people allowed to have any secrets? Is any degree of privacy still allowed? ‘Secrets are lies’, says the Circle’s leader. And one more: ‘privacy is theft’.
Eggers’ book is a timely warning. We already live in an age where large companies have a large influence on our lives, and where individual technologies control more of our behaviour than we should like. Smartphone users, it seems, check their device up to 150 times a day. The only way to prevent a Circle-like dystopia is to protect ourselves. To turn off our smartphones. To disconnect from time to time, and to spend time in nature or with friends. Technology only takes over as much of our life as we allow it.